Introduction
Ever wondered how the internet works? No, it’s not magic, though it might seem like it sometimes! At the heart of all online communication lies the concept of IP addresses. These digital addresses are the backbone of the network. Allowing devices to connect and communicate. But not all IP addresses are equal. Enter IPv4 and IPv6. If you’ve stumbled upon the phrase https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion/. Let’s dive into the nitty-gritty of these two protocols and see what sets them apart!
The Basics: What Are https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion?
IPv4: The Old Reliable
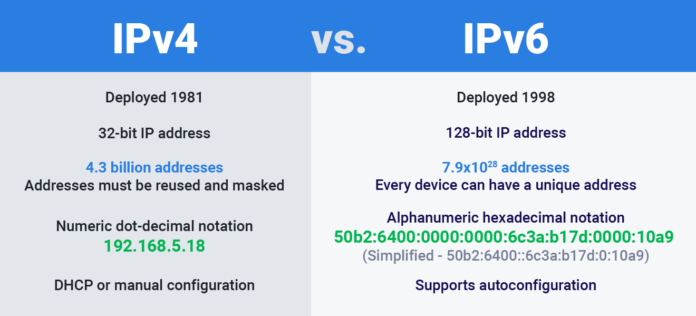
https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion 4. It’s the OG of internet protocols, having been around since the early days of the internet. Here’s a quick rundown:
-
32-bit Address: IPv4 uses a 32-bit address scheme. Which means it can support around 4.3 billion unique addresses. Sounds like a lot, right? But with the explosion of internet-connected devices, it’s actually not enough.
-
Numeric Addressing: IPv4 addresses in decimal as four numbers separated by periods (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
IPv6: The New Kid on the Block
IPv6 is the latest version of the Internet Protocol designed to replace IPv4. Here’s what you need to know:
-
128-bit Address: https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion which supports. An almost inconceivable number of addresses (340 undecillion, to be precise).
-
Hexadecimal Addressing: IPv6 addresses are in hexadecimal and separated by colons. (E.G., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
Key Differences Between https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion
Address Space
The most obvious difference is the address space. IPv4’s 32-bit system is running out of steam, while IPv6’s 128-bit system provides. An unlimited number of addresses. This expansion is crucial for the continued growth of the internet. Especially with the advent of IoT devices.
Security
Security is another biggie. IPv6 with security in mind. It includes IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) as a mandatory component. Ensuring encrypted communication and improved security protocols. IPv4 requires extra configurations to put in place similar security measures.
Configuration
https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion. (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) to assign addresses. IPv6 simplifies this with auto-configuration capabilities. When a device connects to a network, it generates a unique IP address using its MAC address.
Performance
IPv6 can handle packets better than IPv4. The streamlined header of IPv6 improves routing efficiency. Making data transfer faster and more reliable.
Compatibility
One of the biggest hurdles for IPv6 adoption is compatibility. Many devices and networks still rely on IPv4. Transition mechanisms, like dual-stack (running IPv4 and IPv6) and tunneling (encapsulating. IPv6 packets within IPv4), help bridge this gap, but they’re not perfect solutions.
Why the Shift from https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion?
The Looming IP Address Exhaustion
IPv4 addresses are running out. With the explosion of internet-enabled devices, we’ve run out of unique addresses. IPv6 addresses this problem by providing a larger address pool.
Improved Security Features
Built-in IPsec in IPv6 means better security for all devices. In a world where cyber threats are evolving, this is a significant advantage.
Better Performance and Efficiency
IPv6’s efficient routing and handling of packets lead to better performance. This is critical for real-time applications like video streaming and online gaming. Even minor delays can ruin the experience.
Simplified Network Configuration
Auto-configuration capabilities make IPv6 networks easier to manage. This is a boon for both home users and network administrators.
Challenges in Adopting IPv6
Compatibility Issues
Not all devices and networks are IPv6-ready. This can lead to connectivity issues and requirements. The use of transition technologies like dual-stack and tunneling.
Cost of Implementation
Upgrading to IPv6 can be costly. It involves updating hardware, software, and network infrastructure. For many organizations, this is a significant investment.
Learning Curve
There’s a learning curve associated with IPv6. Network administrators and IT professionals need to familiarize themselves with the new protocol. Which can be time-consuming.
FAQs about https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion
1. Can IPv4 and https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion?
Many networks run both IPv4 and IPv6 using a technique called dual-stack. This ensures compatibility and a smooth transition.
2. Will IPv6 completely replace IPv4?
yes. But this transition will take time. For now, both protocols will continue to coexist.
3. Do I need to do anything to use IPv6?
Most modern devices and operating systems support IPv6 right out of the box. Yet, ensuring your network infrastructure (routers, modems, etc.) is IPv6-compatible is crucial.
4. Is IPv6 faster than IPv4?
In some cases, yes. IPv6’s efficient routing and simplified header can lead to better performance. Especially in networks with heavy traffic.
Conclusion
The comparison between https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion highlights. The need for progress in internet protocols. IPv6 addresses the limitations of IPv4. Offering better performance, enhanced security, and unlimited address space. While the transition comes with challenges, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. As more devices connect to the internet,. The shift to IPv6 is not desirable but necessary. So, next time you’re setting up a network or troubleshooting connectivity issues,. Remember the pivotal role that IPv4 and IPv6 play in keeping the digital world connected?
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or curious about the nuts and bolts of the internet,. Understanding these protocols gives you a glimpse into the ever-evolving landscape of technology. Here’s to a future where every device, big or small, has its own place in the vast expanse of the internet!